Wednesday, June 19, 2019
Reference Architecture - Windows Failover Cluster - Two Nodes Multi-Site
Introduction
Friday, December 26, 2014
Using The Command Line To Upgrade Windows Edition
Thursday, October 23, 2014
Windows Server 2012 Deduplication - Powershell Reference
- There is a scheduler which runs one deduplication job / operation at any point in time
- Powershell and windows commands add jobs to the scheduler queue - only one job may run at a given point in time
- Types of deduplication operations:
- Optimization - deduplicates files on the filesystem.
- Scrubbing - performs an integrity check of the deduplication store
- GarbageCollection - files deleted from the filesystem do not automatically free up space on the disk. A garbage collection must be run to clean up the dedupe store
- You can configure the minimum age of files to deduplicate. Typically this should be set to a value greater than one day to ensure active files are not deduplicated.
Here are some handy powershell commands for managing deduplication on Windows Server 2012:
Thursday, May 29, 2014
Renew A Windows Server Group Membership Without Rebooting
Wednesday, February 26, 2014
Deploying A SQL 2012 AlwaysOn Cluster
Friday, February 21, 2014
Building A Windows Cluster Using Windows Server 2008 R2
Saturday, February 1, 2014
Upgrading Powershell on Windows Server 2008 R2
The latest version of Powershell, version 4, has been released by Microsoft in late October 2013. It brings a lot of additional functionality and performance improvements to the table. This document covers how to upgrade Powershell from your current version to Powershell 4.0.
Saturday, March 23, 2013
Install HyperV And Your Networking Dies!!!
The cause of the problem is that when you install Hyper-V it completely reconfigures your networking. Firstly, it will create a "Network Bridge" which is used for to provide virtual networking to your virtual machines. The "Network Bridge" completely takes over your network card. In it's place a virtual network card is installed on your Hyper-V host for host communications.
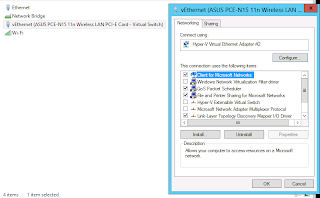
So the first step is to confirm your network settings on the virtual network card which is typically labelled vEthernet (Followed by the physical network card details).
In my case these settings were all fine. My problem resided in my virtual network card settings. First right click on the virtual network card and go into it's properties.
Next click on the configure button just below the network card.
In the advanced tab select the IPv4 Large Send Offload settings and set it as disabled.
Wednesday, January 23, 2013
Securely Wiping An Old Hard Disk
The best way to make sure your private information stays safe is to wipe the hard disk before throwing it in the trash. There's a number of free tools out there to do this. If you're running Windows then a great utility is Disk Wipe.
It's a free download and very, very easy to use. After installing you just run the program and select the drive you want to wipe. Be very, very careful and make sure you select the right drive, there's no way to get this data back once it's wiped. Also make sure you've backed up everything you need before doing this - there ain't no turning back!
The next option to select is the level of wipe you want to do. The option at the top is both the fastest wipe and least secure, the option at the bottom is the slowest wipe and most secure. Typically I select one of the options in the middle - it's a good tradeoff between speed and security. If you're paranoid, select the bottom option and come back in a day - it takes a while!
Wednesday, January 9, 2013
Using NAGIOS to Check the Physical Memory Available on a Windows Host
This is where the NRPE plugins are much better as you can get much more granular when monitoring the memory on a Windows host.
To start with we need to create a new command definition. Add this to your commands.cfg (or equivalent):
# CheckWindowsPhysical Mem command definition
define command {
command_name CheckWindowsPhysicalMem
command_line $USER1$/check_nrpe -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -p 5666 -c CheckMEM -a MaxWarn=$ARG1$% MaxCrit=$ARG2$% ShowAll type=physical
}
# Service definition
# Add the service to the service definition
define service {
service_description Physical Memory
check_command CheckWindowsPhysicalMem!80!90
host_name << hostname >>
event_handler_enabled 0
active_checks_enabled 1
passive_checks_enabled 0
notifications_enabled 1
check_freshness 0
freshness_threshold 86400
use << service template >>
}
You will need to update the above snippet with the host name you are monitoring and the service template you are using. The !80!90 is the standard warning at 80% usage, critical at 90% usage. These can be varied to suit your host and environment.
Wednesday, July 11, 2012
Troubleshooting A Failing MSI Install
So I was installing an application the other day when I got the following error message:
The installer was interrupted before Application could be installed. You need to restart the installer to try again.
Click "Close" to exit.
Not very helpful huh? Luckily there’s a way to get more information. It involves running the msiexec command explicitly so that it generates a logfile with more details on how the execution failed. The command looks like this:
msiexec /package <package.msi>" /l*vx "c:\setup.log"
The /l switch tells msiexec to log installation information to the logfile specified. A lot of information can get piped into this logfile but nonetheless its a handy way to find out what’s happening inside the installation process.
Wednesday, December 28, 2011
Clients Not Showing Up In WSUS
Rem - Batch script to delete duplicate SusClientIDs Rem - Implement this script as a "Startup" or "Logon" script Rem - Script creates an output file called %Systemdrive%\SUSClientID.log Rem - If the %Systemdrive%\SUSClientID.log is already present, then the script simply exits @Echo off if exist %systemdrive%\SUSClientID.log goto end net stop wuauserv net stop bits reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WindowsUpdate" /v PingID /f > %systemdrive%\SUSClientID.log 2>&1 reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WindowsUpdate" /v AccountDomainSid /f >> %systemdrive%\SUSClientID.log 2>&1 reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WindowsUpdate" /v SusClientId /f >> %systemdrive%\SUSClientID.log 2>&1 net start wuauserv wuauclt.exe /resetauthorization /detectnow :end exit
Using Windows Command Line To Manage User Accounts
I’ve been doing some work on a Windows Core box and needed to modify some user accounts. As there’s no GUI the command line is the only way to go.
First up, I wanted to find which users exist in the domain. The dsquery command is used to query the Active Directory objects. Putting user at the end of it filters the object type so only user objects are returned:
dsquery user
To filter it down by username we can add the –name directive to filter the results
dsquery user -name Bob*
And finally I wanted to change the password on a user account. The dsmod command is used to modify Active Directory objects. After using the second command above to find the full user DN I was looking for I ran the following command:
dsmod user "CN=username,OU=Users,OU=Company,DC=Domain,DC=local" -pwd <new Password>
How To Delete hiberfil.sys On Windows Server 2008
Hiberfil.sys is a Windows system file used by the hibernation feature. Whenever you hibernate your computer it’s memory contents are written to this file allowing you to quickly resume your computer.
Typically on a server this feature isn’t useful. Although it’s not enabled by default the hiberfil.sys file exists by default and uses several GB of disk space (depending on how much RAM you have installed). As it’s a system file it’s protected and you can’t just delete it. Instead you have to use the following command to remove it:
powercfg -h off
Wednesday, December 21, 2011
Enable Ping Response In Windows Firewall
Note: This post applies to Windows 7.
By default the Windows Firewall will block any ping requests made to the host. To enable a ping response we need to add a rule to the firewall. First go to Control Panel –> Windows Firewall. On the left hand side select Advanced Settings.
Select the Inbound Rules. Sort the rules by name and find File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request – ICMPv4-In). There’s typically 3 versions of this rule, one for each “network” defined in Windows. Enable this rule for the required networks.
Just some background – ping requests work using a special network protocol called ICMP. ICMP is a network management protocol and an Echo Request is a type of packet set via ICMP used to determine if a host is up or down (and indicate the response time). Often these ping requests are discarded in order to tighten security. One of the first thing potential hackers may do is ping an IP address to determine if the machine is “on” before trying anything further.
Tuesday, December 20, 2011
Error 2738 Occurs When Installing An MSI Package
This occurs when there’s a problem running vbscript with elevated permissions. To confirm that its the problem run the MSI installer from the command line (with administrator permissions – right click on the command prompt link in the start menu and select run as administrator) like this:
MSIEXEC /i <msi package> /lv log.txt
Once the error occurs open the log file and look for the following output:
DEBUG: Error 2738: Could not access VBScript runtime for custom action We need to re-register the vbscript dll for this error to be resolved. First step is to remove the old registration by deleting the registry key:
# 32 bit windows
HKCU\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{B54F3741-5B07-11CF-A4B0-00AA004A55E8}
# 64 bit windows
HKCU\SOFTWARE\Classes\Wow6432Node\CLSID\{B54F3741-5B07-11CF-A4B0-00AA004A55E8}
Once this is done you need to re-register the DLL using the following command:
# 32 bit windows
cd %windir%\system32
regsvr32.exe vbscript.dll
# 64 bit windows
cd %windir%\ syswow64
regsvr32.exe vbscript.dll
Saturday, December 17, 2011
Removing GRUB and Restoring the Windows Boot Loader
Note: This has been tested with Windows Vista
In this post we’ll be using the Windows Vista boot disk to restore the boot loader.
- Insert the Windows Vista installation disk into your CD \ DVD Rom drive
- Boot your computer, when prompted press any key to enter the installation
- Confirm your language and input settings and click Next
- Click Repair Your Computer
- Select the operating system you want to keep and click on Next
- In the System Recovery Options click on Command Prompt
- In the command prompt type Bootrec.exe /fixmbr and press enter. The message “Operating completed successfully” will be displayed once the command has finished running.
- Now reboot your computer
And voila – the GRUB boot loader has now been replaced with the Windows boot loader. If you haven’t done so already you will want to remove your old Linux partitions and recover your disk space.